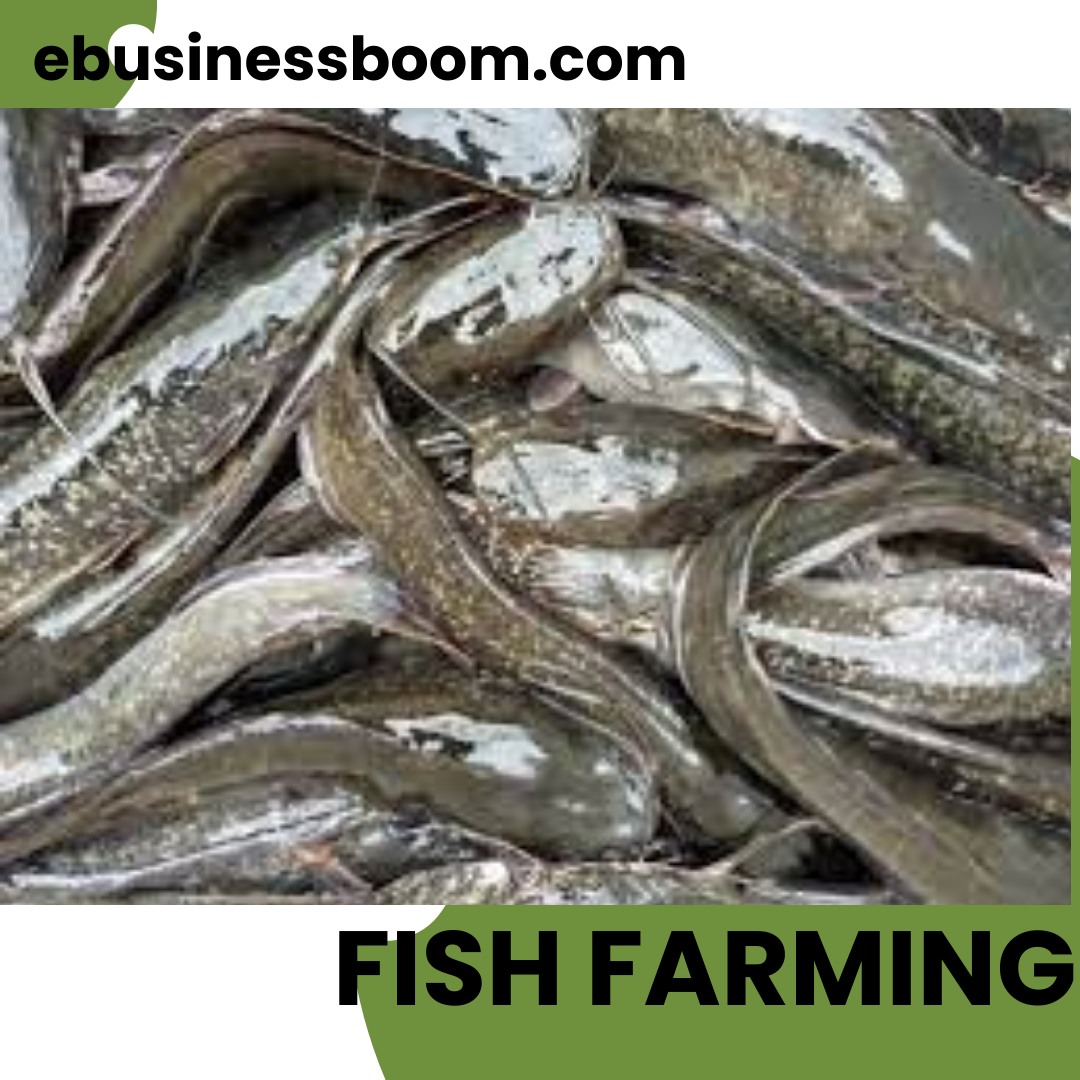
Fish farming is one of the most common agribusiness in Nigeria. gone are those days when catching fish in the local rivers is the only means of getting fish and required a lot of trial and error. Today, it is possible to manage the input and raise fish in farms thanks to advanced farming techniques.
Catfish Farming
Catfish farming is a good business to start right now, in my opinion. I would suggest you start fish farming if you’re looking for a lucrative Agribusiness or adding fish farming to your business if you are an established farmer trying to increase the size of your farm. especially catfish farming, is most compatible with poultry farming since you can feed your fish with the poultry droppings.
Fish Farming
Fish farming, also known as aquaculture, is a lucrative and sustainable business opportunity in Nigeria. With its abundant water resources and high demand for fish products, Nigeria provides favorable conditions for aspiring fish farmers. In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through the stages involved in starting a successful fish farming business in Nigeria, from production to marketing.
How to start Fish Farming
Stage 1: Planning and Research
Site Selection: Identify a suitable location for your fish farm, considering factors such as access to water sources, soil quality, proximity to markets, and availability of infrastructure. Since fish don’t disrupt the ecosystem, any site is suitable. Find land that you can purchase for a reasonable price. A half-plot of land is sufficient for an ordinary fish farm, depending on the capacity you wish to run at.
If you can afford it, you might choose a larger option—perhaps a full plot or two—most likely for convenience’s sake. You may use any extra space in your compound that you believe can house two or three ponds.
Fish Species
Identify the Fish Species: Determine the fish species that are suitable for your farming goals, considering factors such as market demand, climate compatibility, growth rate, and profitability. Popular fish species in Nigeria include catfish (Clarias gariepinus) and tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus).
Choose the Farming System: Select the appropriate farming system based on your resources and goals. Common options include pond farming, recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS), or cage farming in natural water bodies.
Acquire Knowledge and Training: Seek out training programs or workshops specific to fish farming in Nigeria. Not the kind of training you obtain from one-day seminars; for an appropriate apprenticeship, you must become a part of a fish farm or be under guidance of a successful fish farmer, you need at least two months of learning in order to learn this trade successfully.
Keep in mind that your investment is at risk; in business, trial and error rarely pays off unless you have unlimited resources at your disposal. Gain knowledge about pond construction, water quality management, feeding practices, disease prevention, and record-keeping. Consulting with experienced fish farmers and agricultural extension services can provide valuable insights.
Stage 2: Farm Setup and Production
After selecting proper site for your fish farming, considering factors such as access to water sources either by digging borehole or any other proper means, soil quality, proximity to markets, and availability of infrastructure.
Pond Construction: Construct fishponds either Concrete one or earthen pond or install fish cages according to the farming system chosen. Ensure proper pond design, water supply, and drainage systems. Optimize the size and depth of the ponds to accommodate the desired fish stocking density. You can engage the service of expert pond construction engineer or you go to another fish farm to get the specification and construction requirements. The plumbing work must be properly done to ensure proper drainage.
Fish Stocking: Procure fingerlings or juvenile fish from reputable hatcheries. Introduce the fish into the ponds or cages following recommended stocking densities. Monitor water parameters such as temperature, pH, and oxygen levels to maintain optimal conditions for the fish.
Feeding and Nutrition: Provide a well-balanced diet for the fish, including commercial fish feed or locally available feed ingredients. Monitor feeding practices, adjust feed amounts as the fish grow, and ensure consistent feed quality and supply.
Water Management and Health: Maintain proper water quality by monitoring oxygen levels, temperature, pH, and ammonia levels. Regularly inspect the fish for signs of diseases or stress. Implement appropriate disease prevention measures, including quarantine protocols, vaccinations, and good farm hygiene practices.
Stage 3: Harvesting and Processing
Growth Monitoring: Regularly monitor the growth and health of the fish by measuring weight, length, and overall condition. Adjust feeding practices and management strategies accordingly to optimize growth rates.
Harvesting: Plan the harvesting process based on market demand and the fish’s desired size. Use appropriate harvesting methods, such as seining, netting, or draining the pond. Minimize stress to the fish during the harvesting process to maintain product quality.
Processing and Packaging: Clean and process the harvested fish promptly. Remove scales, gut the fish, and clean them thoroughly. Package the fish in suitable materials to preserve freshness and quality, consider value-added processing options, such as filleting, smoking, or freezing, to diversify your product range.
Stage 4: Marketing and Sales
Identify Target Markets: Identify potential buyers, including wholesalers, retailers, restaurants, or individual consumers. Research market trends, pricing, and preferences to understand the demands and expectations of your target customers.
Build a Brand and Distribution Network: Develop a strong brand presence by creating a unique identity for your fish farm. Establish relationships with distributors, local markets, and potential buyers. Utilize digital platforms, social media, and local trade fairs to promote your products and expand your customer base.
Pricing and Selling Strategies: Set competitive pricing based on production costs, market value, and product quality, consider factors such as transportation costs, packaging, and market competition. Develop effective selling strategies, including offering discounts, incentives, or tailored products to meet specific customer demands.
Customer Service and Feedback: Provide excellent customer service, ensuring timely delivery, product quality, and responsiveness to customer inquiries. Encourage feedback from customers to understand their preferences and improve your products and services.
Conclusion: Starting a fish farming business in Nigeria offers tremendous opportunities for aspiring entrepreneurs. By carefully planning and researching, setting up the farm, managing production, and implementing effective marketing strategies, you can establish a successful fish farming venture. Remember to stay updated with industry trends, adopt best practices, and continuously improve your operations to ensure the long-term sustainability and profitability of your fish farm. With dedication, perseverance, and a passion for aquaculture, your fish farming business in Nigeria can thrive and contribute to both economic growth and food security. Best of luck on your journey!








One Response